The ultimate goal is to develop treatments that not only manage symptoms but also address the genetic root of the disorder.
While genetic factors lay the foundation for our inherent characteristics, the influence of lifestyle choices on our health is a dynamic and critical aspect. The interplay between genetics and lifestyle can significantly impact the development and progression of genetic disorders. In this article, we will discuss about one such disorder Cystic Fibrosis. To subscribe please click tau.id/2iy6f and access our live channel.
DON’T MISS: New Method Allows Heart to Grow Within Body
What is Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. It is a lifelong condition that significantly impacts the quality of life. It is a genetic condition that affects a protein in the body. People who have cystic fibrosis have a faulty protein that affects the body’s cells, its tissues, and the glands that make mucus and sweat.
What is Genetic Disorder
Genetic disorders are a diverse group of conditions caused by abnormalities in an individual’s DNA, the genetic blueprint that guides the development and functioning of the human body.
It result from changes or mutations in genes, the functional units of DNA. Mutations can occur spontaneously during conception or be inherited from one or both parents. These disorders can range from mild to severe, affecting various aspects of health and well-being.
Causes or Roots of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease caused by mutations in a gene called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). The CFTR gene encodes a protein responsible for regulating the movement of salt and water in and out of cells.
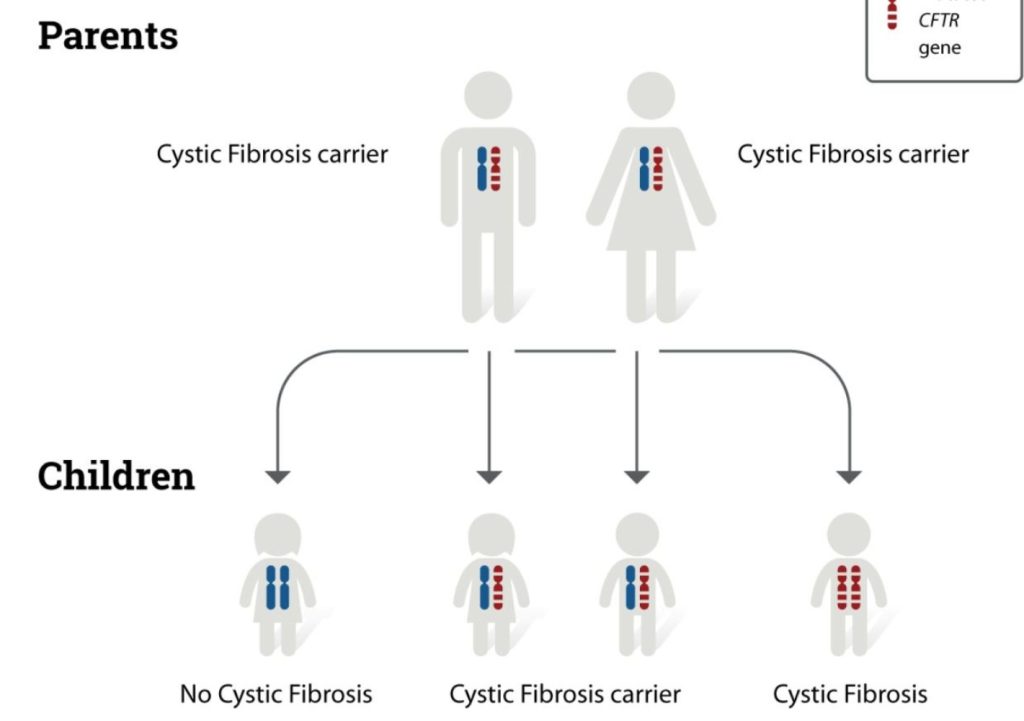
Mutations in this gene lead to the production of a defective CFTR protein, resulting in thick and sticky mucus that can clog airways and various ducts in the body. The inheritance pattern of cystic fibrosis follows an autosomal recessive manner.
Both parents must carry a faulty CFTR gene for a child to inherit the disorder. Individuals with only one mutated gene are carriers and do not exhibit symptoms but can pass the gene to their offspring.
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
Symptoms depend on which organs are affected and how severe the condition is. Some people have few or no symptoms, while others experience severe symptoms or life-threatening complications. Symptoms can get better and worse at different times.
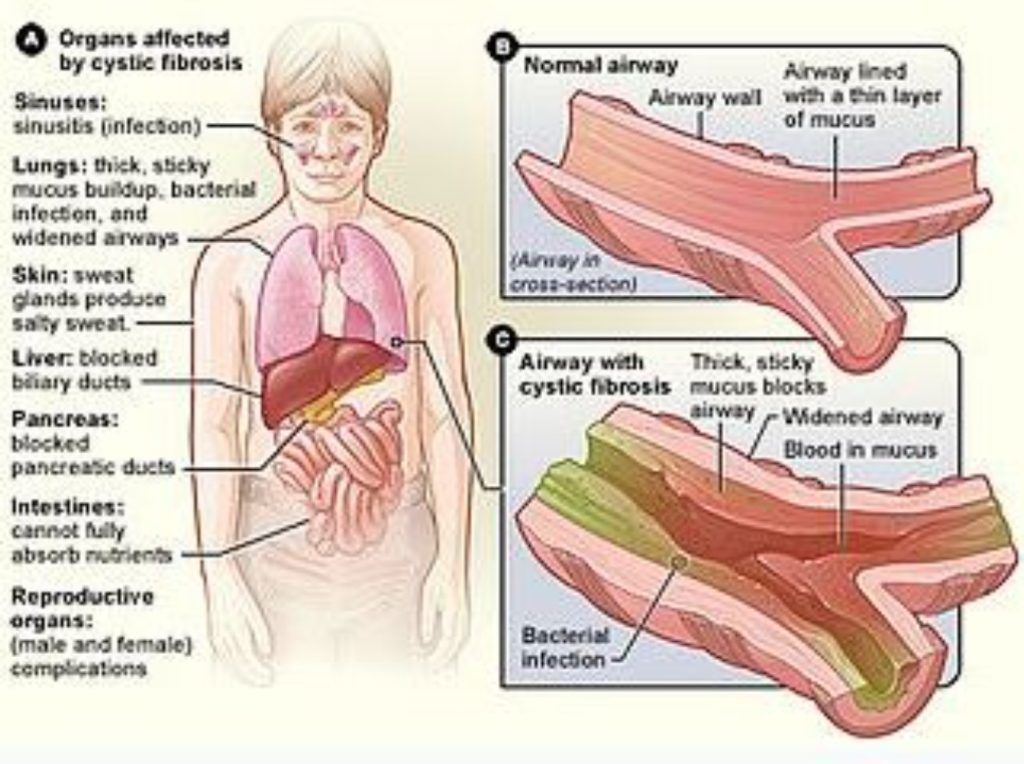
Cystic fibrosis most often affects the lungs. Some people who have cystic fibrosis have wheezing and a cough that can produce mucus or blood. Other symptoms depend on the organs affected and can include:
- Blocked intestine in a baby soon after birth
- Clubbing of fingers and toes due to less oxygen getting to the hands and feet
- Delayed puberty
- Fertility problems, especially for males
- Fever, which may include night sweats
- Gastrointestinal symptoms such as severe belly pain, chronic (long-term) diarrhea, or constipation
- Infections of sinuses and lungs
- Jaundice or yellowing of the skin and eyes, for an abnormally long time after birth
- Low body mass index (BMI) or being underweight
- Muscle and joint pain
- Pancreatitis ( inflammation of the pancreas)
- Salty skin and extra-salty sweat
- Slow growth and shorter height
When To Dial the Emergency Number
Cystic fibrosis may have serious complications. Call your doctor right away if you believe you have any of the following.
- Coughing or spitting up blood may be a sign that an artery has broken and is bleeding into the airway.
- Sudden shortness of breath or chest pain may be a sign of a pneumothorax, or collapsed lung.
- Pulmonary exacerbation involves a worsening of lung symptoms, such as more coughing or wheezing, chest congestion, and a change in mucus color. You may also have weight loss, a poor appetite, or fever.
Preventive Measures
As cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder, it cannot be prevented outright. However, individuals with a family history of CF or those who are carriers can opt for genetic counseling before planning a family.
Understanding the genetic risk allows couples to make informed decisions about family planning and explore options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) with pre-implantation genetic testing.
Additionally, managing environmental factors, such as avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help individuals with cystic fibrosis reduce the risk.
Diagnosing the Disorder
Cystic fibrosis is typically diagnosed through a combination of newborn screening, genetic testing, and clinical evaluations.
Newborn screening involves testing a small blood sample taken from a newborn’s heel. If the initial screening suggests the possibility of CF, further diagnostic tests, such as a sweat test and genetic testing, are performed.
The sweat test is a definitive diagnostic tool for cystic fibrosis. It measures the concentration of salt in the sweat, which tends to be elevated in individuals with CF.
Genetic testing identifies specific mutations in the CFTR gene, confirming the diagnosis and providing information about the severity of the condition.
Preconception and prenatal screening tests use a sample of blood, saliva, or cells from the inside of your cheek to check your DNA.
Current Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for cystic fibrosis, advances in medical care have significantly improved the life expectancy and quality of life for individuals with the condition. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Airway clearance techniques, inhaled medications, and oral antibiotics are commonly used to address respiratory symptoms.
- Enzyme replacement therapy helps individuals with CF digest and absorb nutrients properly, addressing the digestive aspects of the disorder.
- Physical exercise, a nutritious diet, and maintaining optimal lung health are essential components of managing cystic fibrosis.
- Surgery may be needed for people with advanced conditions such as lung transplant may help people with severe lung disease and respiratory failure, or liver transplant may be an option for advanced liver diseases.
The Ongoing Pursuit of A Cure
Researchers and medical professionals continue to explore innovative therapies and potential cures for cystic fibrosis.
Breakthroughs in gene therapy, which involves correcting or replacing the faulty CFTR gene, hold promise for the future.
Trials for drugs targeting the underlying cause of cystic fibrosis are ongoing, with some therapies showing significant success in addressing the defective protein and improving lung function.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, implementing preventive measures, and early diagnosis are crucial components in the fight against Cystic Fibrosis. While there is no cure yet, ongoing research and advancements in medical science offer hope for a future where individuals with cystic fibrosis can lead longer, healthier lives.