The US Department of Energy predicted that lithium demand would increase five to tenfold by 2030. Lithium is already relatively short, and thus expensive.
An Indian-origin scientist, Vijay Murugesan-led team has discovered a new battery material using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and supercomputing that could reduce lithium use in batteries. The findings were made by Microsoft and the US-based Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). To subscribe please click tau.id/2iy6f and access our live channel.
The new battery material came out using Microsoft’s Azure Quantum Elements to narrow down 32 million potential inorganic materials to 18 promising candidates that could be used in battery development in just 80 hours.
ALSO READ: WhatsApp Adds New Feature, Check Details
Since the discovery of the new material, it has been used to power a lightbulb. The AI-derived material is a solid-state electrolyte. According to the scientists, the new material could potentially reduce lithium use by up to 70 per cent.
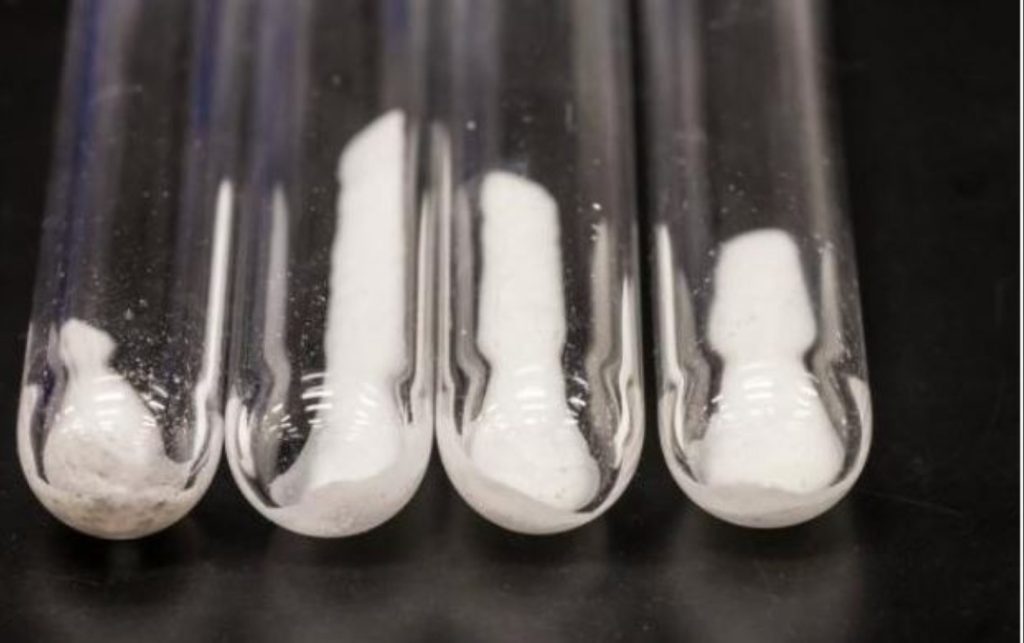

Initially, scientists thought that sodium ions and lithium ions couldn’t be used together in a solid-state electrolyte system because they are similarly charged but have different sizes. But after testing, it was found that the sodium and lithium ions seem to help each other.
Lithium is environmentally and geopolitically problematic. Traditional lithium-ion batteries also pose safety issues, with the potential to catch fire or explode. Many researchers are looking for alternatives, both for lithium and for the materials used as electrolytes.




